How to Give a Vitamin B12 Injection: A Complete Guide
Last updated on December 12th, 2025 at 05:50 pm
How to Give a Vitamin B12 Injection Vitamin B12 is a vital nutrient for diverse physical functions, which include generating crimson blood cells, DNA synthesis, and retaining the nervous system. Many humans are afflicted by Vitamin B12 deficiency because of nutritional regulations, positive clinical conditions, or age-related elements. For these individuals, Vitamin B12 injections provide an effective way to reinforce their B12 degrees.
This guide will cover the whole lot you need to know about the way to supply a Vitamin B12 injection, along with step-by-step commands, dosage, and frequency.
Read More: Lipo B12 Injections, B12 Shots for Weight Loss

Table of Contents
Understanding Vitamin B12
Vitamin B12, also known as cobalamin, is a water-soluble vitamin that plays a critical role in:
- Red blood cell formation
- DNA synthesis
- Nervous system function
- Energy production
Benefits of Vitamin B12
Vitamin B12, also known as cobalamin, is very important for our bodies. Here are some key benefits of Vitamin B12:
Many people start to feel the benefits of B12 injections within 24 to 72 hours after administration. The effects can vary depending on the individual and their level of deficiency.
1. Prevents Anemia: Vitamin B12 helps make healthy red blood cells. Without enough B12, you can get anemia, which makes you feel tired and weak.
2. Boosts Energy Levels: Vitamin B12 can help you feel less tired and give you more energy because it helps turn the food you eat into energy.
3. Supports Brain Health: Vitamin B12 is important for your brain. It helps keep your nerves healthy and can help prevent memory loss and other brain problems.
4. Improves Mood: Vitamin B12 helps make serotonin, a chemical that makes you feel happy. Enough B12 can help improve your mood and reduce depression.
5. Supports Bone Health: Vitamin B12 helps keep your bones strong. Low levels of B12 can make your bones weak and increase the risk of breaking.
6. Promotes Healthy Skin, Hair, and Nails: Vitamin B12 is important for healthy skin, hair, and nails. If you don’t get enough B12, you might have skin problems, weak nails, and hair loss.
7. Supports Heart Health: Vitamin B12 helps lower a substance called homocysteine in your blood, which is good for your heart. High levels of homocysteine can lead to heart problems.
8. Helps with DNA Synthesis: Vitamin B12 is needed to make and repair DNA, which is the genetic material in your cells.
9. Helps with Red Blood Cell Formation and Function: Vitamin B12 is essential for making red blood cells and helps them work properly to carry oxygen in your body.
10. Supports Immune Function: Vitamin B12 helps keep your immune system strong, so you can fight off infections better.
11. Aids Digestive Health: Vitamin B12 helps your digestive system work well and keeps your gut healthy.
Causes of Vitamin B12 Deficiency

- Dietary Restrictions: Vegans and vegetarians are at risk because B12 is primarily found in animal products.
- Medical Conditions: Conditions like Crohn’s disease, celiac disease, and pernicious anemia can affect B12 absorption.
- Age: Older adults may have decreased absorption of B12.
- Medications: Certain medications like metformin and proton pump inhibitors can interfere with B12 absorption.
How Much Vitamin B12 Do We Need?
- For Adults:
- Take 2,000 mcg of cyanocobalamin once a week, ideally as chewable, sublingual, or liquid supplements on an empty stomach.
- Or, take 50 mcg daily of cyanocobalamin as a supplement.
- Eat B12-fortified foods three times a day, each with at least 190% of the Daily Value listed on the label.
- For Adults over 65:
- Take 1,000 mcg of cyanocobalamin every day.
If you have symptoms of B12 deficiency, a urine MMA test is better than checking your B12 blood levels.
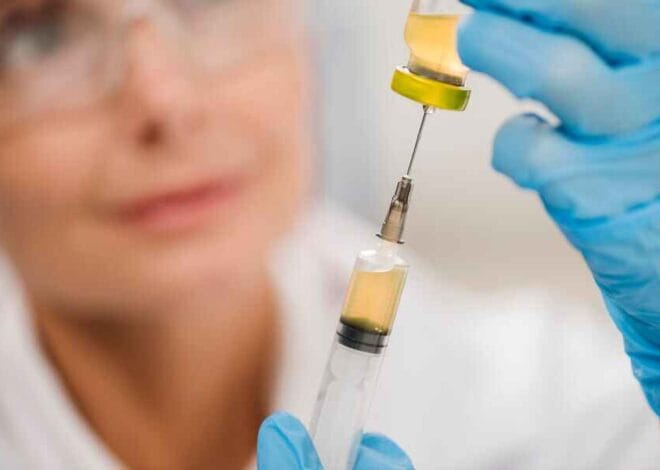
Preparation Before the Injection
Before starting Vitamin B12 injections, it is crucial to consult a healthcare professional. They can determine the appropriate dosage and frequency based on your specific needs.
To give a Vitamin B12 injection, you will need the following supplies:
- Vitamin B12 vial or ampoule
- Syringe and needle (usually 25-27 gauge, 1-inch needle)
- Alcohol wipes
- Cotton ball or gauze
- Bandage
- Sharps disposal container
Choosing the Injection Site
Common sites for administering a Vitamin B12 injection include:
- Thigh (vastus lateralis muscle): Suitable for self-administration.
- Upper arm (deltoid muscle): Suitable for self-administration or help from another person.
- Buttocks (gluteus medius muscle): Typically administered by a healthcare professional.
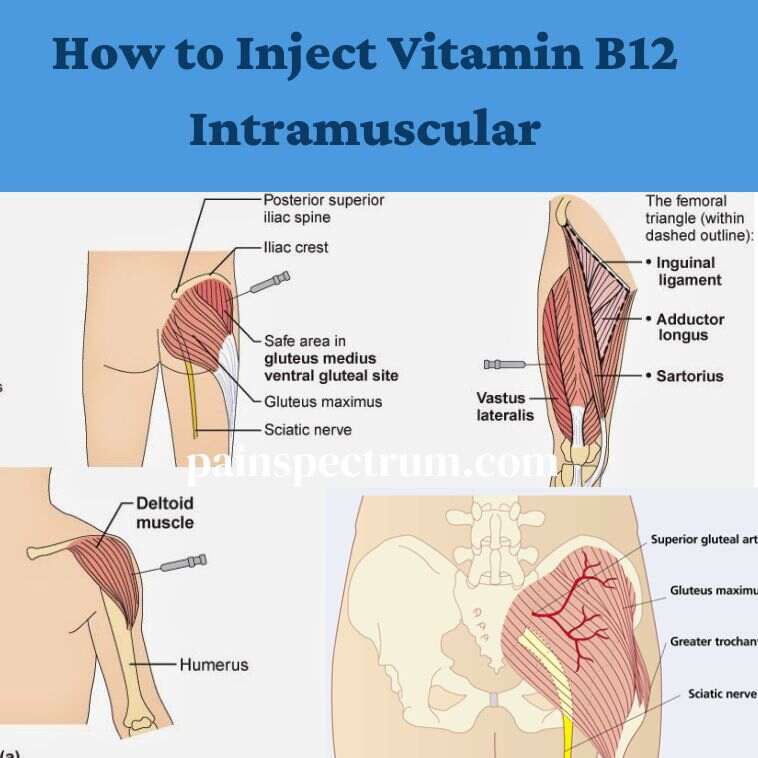
How to Inject Vitamin B12 Intramuscular
Supplies Needed
To give a Vitamin B12 injection, you will need the following supplies:
- Vitamin B12 vial or ampoule
- Syringe and needle (usually 25-27 gauge, 1-inch needle)
- Alcohol wipes
- Cotton ball or gauze
- Bandage
- Sharps disposal container
How to Give a Vitamin B12 Injection Shot in the Buttocks

- Preparation: Follow the general preparation steps (washing hands, preparing the site, drawing the B12).
- Positioning: The person receiving the injection should lie face down or stand with the weight shifted to the opposite leg.
- Injection Site: The upper outer quadrant of the buttocks (gluteus medius muscle) is preferred.
- Administration:
- Clean the site with an alcohol wipe.
- Insert the needle at a 90-degree angle.
- Inject the B12 slowly.
- Remove the needle and apply pressure with gauze.
How to Give B12 Injection in Arm

- Preparation: Follow the general preparation steps.
- Positioning: The person should sit or stand with the arm relaxed.
- Injection Site: The deltoid muscle in the upper arm.
- Administration:
- Clean the site with an alcohol wipe.
- Insert the needle at a 90-degree angle.
- Inject the B12 slowly.
- Remove the needle and apply pressure with gauze.
.
How to Give B12 Injection in Leg
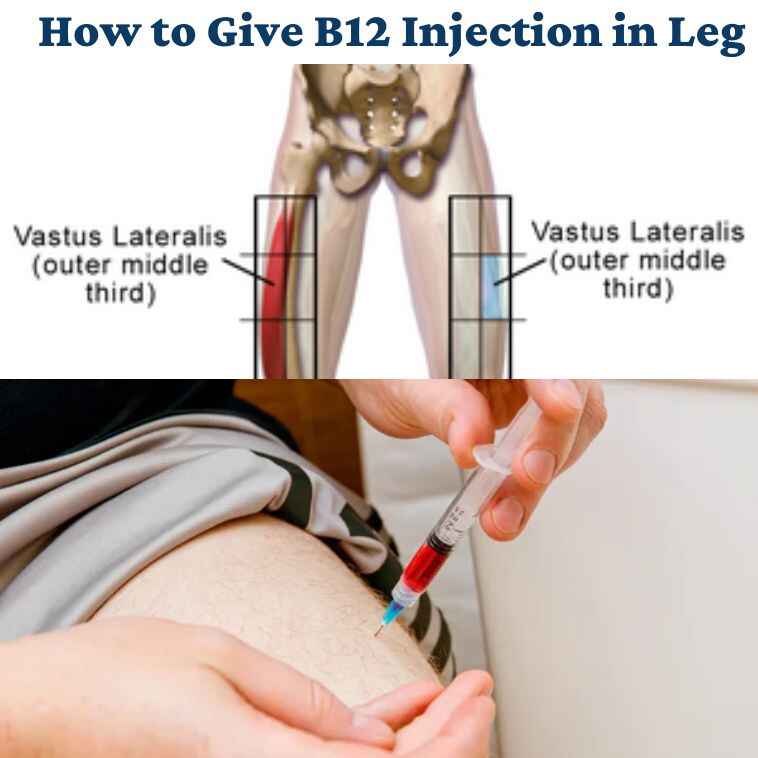
To give a B12 injection in the leg, start by gathering your supplies: a syringe filled with B12, an alcohol swab, cotton or gauze, and a sharps container. Choose the outer thigh muscle (vastus lateralis) for the injection site. Wash your hands and clean the area with the alcohol swab. Hold the syringe with the B12 in one hand and pinch a bit of skin on the thigh with your other hand.
Insert the needle straight into the pinched skin at a 90-degree angle, then slowly push the plunger to inject the B12. Remove the needle and apply pressure with cotton or gauze. Throw away the needle in a sharps container. Watch for any reactions and contact your healthcare provider if needed.
Best Needle for B12 Injection
- Gauge: 25-27 gauge needles are commonly used.
- Length: 1-inch needles are typically sufficient for intramuscular injections.
How to Give Yourself a B12 Shot in the Thigh
- Preparation: Follow the general preparation steps.
- Choosing a Site: The thigh (vastus lateralis muscle) is recommended for self-administration.
- Technique:
- Clean the injection site thoroughly with an alcohol wipe.
- Insert the needle at a 90-degree angle into the thigh.
- Inject the Vitamin B12 slowly and steadily.
- After injecting, swiftly remove the needle and apply gentle pressure with gauze.
Where is the Best Place to Give a B12 Injection?
The best places to give a B12 injection are:
- Thigh (vastus lateralis muscle): Suitable for self-administration.
- Upper arm (deltoid muscle): Suitable for self-administration or help from another person.
- Buttocks (gluteus medius muscle): Typically administered by a healthcare professional.
What Happens if You Inject B12 Wrong?
Injecting B12 incorrectly can lead to:
- Pain or discomfort at the injection site
- Bruising or bleeding
- Infection if proper hygiene is not maintained
- Ineffective absorption of vitamin
Are B12 Injections Intramuscular or Subcutaneous?
Vitamin B12 injections can be administered either intramuscularly (IM) or subcutaneously (SC). The choice of method depends on the patient’s condition, doctor’s preference, and sometimes the specific type of B12 preparation used.
- Intramuscular (IM) Injections: These are administered deep into a muscle, typically the upper arm, thigh, or buttock. IM injections are commonly used and can be more effective for certain conditions because the muscle tissue has a good blood supply, which helps with the rapid absorption of vitamins.
- Subcutaneous (SC) Injections: These are administered into the fat layer beneath the skin. Common sites for SC injections include the abdomen or thigh. This method is also effective and is sometimes preferred for ease of self-administration.
How to Inject a B12 Shot at Home
First and foremost, it’s crucial to meet with your doctor before proceeding with anything else.
- Gather Supplies: Ensure you have the necessary supplies.
- Prepare the Injection Site: Clean the site with an alcohol wipe.
- Draw the Vitamin B12: Follow the steps to draw the B12 into the syringe.
- Administer the Injection: Insert the needle and inject the B12 slowly.
- Dispose of the Needle: Use a sharps container for disposal.
What Not to Do After a B12 Injection?
After getting a B12 injection, following a few simple rules to stay safe and let the injection work well is important. First, try not to do any heavy exercise right after the injection. This can help you avoid pain or irritation where the needle went in. It’s also a good idea to avoid drinking alcohol for a few hours after the injection. Alcohol can stop your body from absorbing the B12 properly.
Another thing to remember is not to touch or rub the place where you got the injection. This can make it sore or cause an infection. If you feel dizzy or light-headed after the injection, it’s best not to drive or use machines until you feel better. Lastly, make sure to follow any other advice your doctor gives you. They might want you to come back for another appointment or watch for any problems. Following these tips will help you get the most out of your B12 injection and keep you safe.
How Soon Do You Feel Less Tired After a B12 Injection?
After receiving a B12 injection, some individuals may start feeling less tired within a few days. However, the exact timeframe can vary from person to person. Consistently receiving B12 injections as prescribed by your healthcare provider is typically necessary to experience sustained improvements in energy levels over time.
What Happens if You Inject B12 into the Vein?
Injecting B12 into a vein (intravenously) can lead to rapid absorption of the vitamin into the bloodstream. This can potentially cause adverse effects because the body might absorb more B12 than it needs at once. It’s generally recommended to administer B12 injections into the muscle (intramuscularly) to ensure a controlled release and absorption over time. If B12 is accidentally injected into a vein, it’s important to seek medical attention promptly to monitor for any complications and ensure appropriate management.
Why Do I Feel Weird After a B12 Injection?
- Mild Side Effects: Some people may experience mild dizziness, nausea, or lightheadedness after a B12 injection.
- Consult a Professional: If these symptoms persist or worsen, consult a healthcare professional.
Does B12 Need to Be Refrigerated?
- Storage Instructions: Store Vitamin B12 at room temperature, away from direct sunlight. Some formulations may require refrigeration—always check the label.
Is It OK to Inject B12 Daily?
Yes, it’s okay to inject vitamin B12 daily if your doctor recommends it, especially if you have a severe deficiency or certain health conditions. Vitamin B12 is safe in high doses because any extra is usually flushed out of the body in urine. Always follow your doctor’s advice for how often to get injections and how much to take.
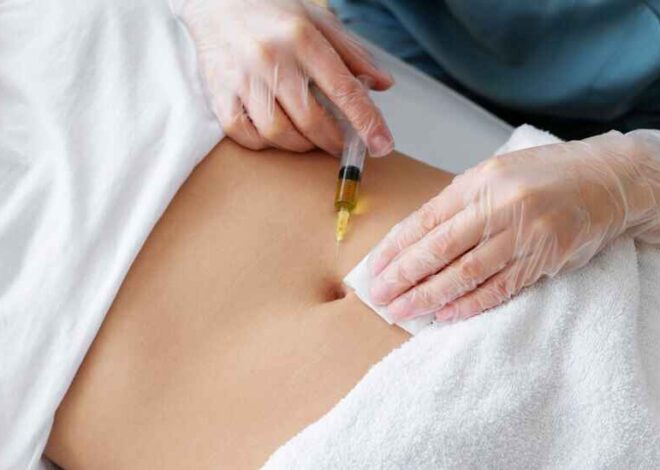
Can You Inject B12 in Belly Fat?
Yes, you can inject vitamin B12 into belly fat. It’s a common and safe way to administer the vitamin. Before injecting, clean the area and pinch a bit of skin to insert the needle. Push the plunger to deliver the vitamin B12. Afterward, apply gentle pressure and dispose of the needle properly. Always follow your doctor’s instructions for the right dosage and technique.
What Happens if You Accidentally Inject Air into Muscle?
Accidentally injecting a small amount of air into a muscle is usually not dangerous. Our bodies can handle small air bubbles without problems. Medical professionals take steps to prevent this by checking the syringe before injecting. They might pull back the plunger slightly to make sure no blood enters, which could mean the needle is in a blood vessel. If only a tiny bit of air gets injected, it usually dissolves in the bloodstream or is absorbed by nearby tissues.
However, injecting a larger amount of air can be more serious. It could cause an air bubble to block a blood vessel, which might lead to problems like trouble breathing or chest pain. This is rare with muscle injections but more of a concern with injections into veins. If someone has worries or feels unusual after an injection, it’s best to get medical help right away.
Is It Okay to Inject B12 Subcutaneously?
Yes, it is okay to inject B12 subcutaneously, meaning into the fatty layer of tissue just beneath the skin. Subcutaneous injections of B12 can be effective and are often administered in medical settings based on healthcare provider recommendations. This method allows for gradual absorption of the vitamin into the bloodstream. It’s important to follow your healthcare provider’s guidance regarding the appropriate injection technique and site for subcutaneous administration of B12.
What Happens if You Don’t Inject B12 into the Muscle?
If you inject B12 into the wrong place, like under the skin instead of into the muscle, it can cause problems. The B12 might not absorb as well into your body, which means it might not work as effectively. Also, it could be more uncomfortable than if it’s injected correctly into the muscle. B12 injections are meant to be given into the muscle for the best results. Always follow your doctor’s instructions on how and where to inject B12 to make sure you get the most benefit from it.
FAQ Section
What is Vitamin B12 and why is it important?
Vitamin B12 is a crucial nutrient involved in red blood cell formation, DNA synthesis, and nervous system function. It helps prevent anemia and boosts energy levels.
How do I prepare for a Vitamin B12 injection?
Consult a healthcare professional, gather necessary supplies (syringe, needle, alcohol wipes, etc.), and choose a clean, suitable injection site.
Can I give myself a Vitamin B12 injection?
Yes, with proper training and guidance from a healthcare professional, self-administration is possible.
Where should I inject Vitamin B12?
Common sites include the thigh, upper arm, and buttocks. Consult with your healthcare provider for the best site for you.
Are there any side effects?
Mild side effects include pain or redness at the injection site, itching, or swelling. Severe reactions are rare but require immediate medical attention.
Do You Inject B12 Fast or Slow?
Inject the B12 slowly to minimize discomfort and ensure proper absorption. A slow injection allows the muscle to absorb the Vitamin B12 more effectively.
What Size Needle Should Be Used for B12 Injections?
- Gauge: 25-27 gauge needles.
- Length: 1-inch needles for intramuscular injections.
Conclusion
Administering a Vitamin B12 injection may seem daunting at first, but with the right preparation and guidance, it can be done safely and effectively. Always consult with a healthcare professional before starting any injection regimen and follow their instructions carefully. Remember to maintain hygiene, use the correct technique, and monitor for any side effects. By following this comprehensive guide, you can ensure that you or your loved ones receive the full benefits of Vitamin B12 injections.
Disclaimer:
The information provided in this article has been verified from reliable sources. However, medical and health information is subject to change, and readers are advised to consult health professionals for specific guidance and advice This article is for informational purposes only and is not intended to be a substitute for professional medical advice or treatment.