Burning Knee Pain 8 Causes and Best Treatment Options
Last updated on January 29th, 2026 at 03:27 am
The knee is one of the most used joints in the body. Whether you realize it or not, almost every movement we make involves the knee. Various issues, such as arthritis, gout, or injuries to muscles and ligaments can cause a burning sensation in the knee.
Burning pain in the knee is unexpected and very unpleasant. It may feel like your joint is on fire, or like something sharp is poking it. This constant burning sensation can make walking, resting, or even sleeping hard. If you’re tired or injured, the pain can get worse.
In most cases, burning knee pain is a sign of something wrong with the joint. However, it could also indicate other complications, so getting the correct diagnosis is essential to avoid further problems. Sometimes, it’s just the result of overuse or an untreated injury, which simply needs proper rest.
This article will cover the common causes of burning knee pain, treatments, and when you should see a doctor.
Read More:
harp, Stabbing Pain in Knee that Comes and Goes
Table of Contents
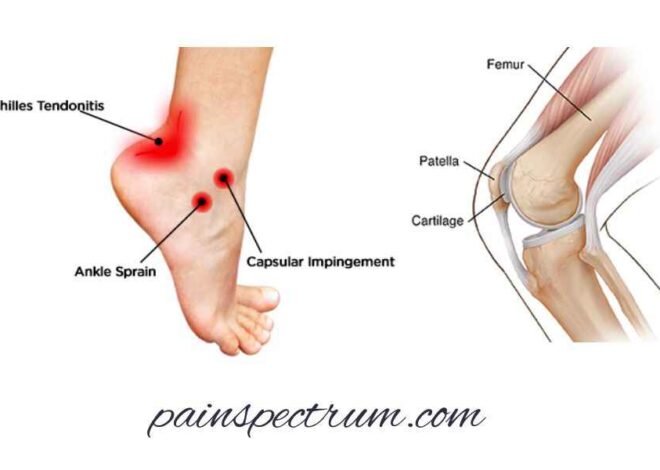
Location of the burning knee pain
Feeling a burning pain in different parts of the knee can help identify the cause. Here’s a simple guide to potential reasons based on where you feel the pain:
Read More:
Knee Pain Location Chart

Front of the Knee:
Burning pain at the front of the knee could be due to:
- Tendonitis: Inflammation of tendons
- Chondromalacia: Softening of the cartilage under the kneecap
- Patellofemoral Pain Syndrome: Pain around the kneecap
- Bursitis: Inflammation of the fluid-filled sacs in the knee
- Arthritis: Joint inflammation
- Nerve Injury: Issues with nerves like neuropathy or neuritis
Side of the Knee:
Burning pain on the side of the knee might be caused by:
- Iliotibial Band Syndrome: Irritation of the band running from the hip to the shin
- Pes Anserine Bursitis: Inflammation of a bursa (fluid-filled sac) on the inside of the knee
Back of the Knee:
Burning pain at the back of the knee could be due to:
- Overuse: Excessive use of the knee
- Ligament Tear: Tear of knee ligaments
- Cartilage Tear: Tear of the knee cartilage
- Baker’s Cyst: Fluid-filled swelling behind the knee
Causes and Treatments of Burning Knee Pain
Here’s a breakdown of possible causes and treatments for burning knee pain:
1. Torn Knee Cartilage
The knee cartilage, or meniscus, helps cushion the joint during activities like walking, running, and jumping. If the knee is subjected to a strong impact or twisted forcefully, the cartilage can tear, causing pain or a burning sensation.
Treatment for Torn Cartilage:
- Over-the-counter pain relievers like ibuprofen
- Rest
- Exercises to strengthen muscles
- If symptoms persist, a doctor might suggest:
- Knee cleaning: Removing loose cartilage and washing the area with saline
- Smoothing cartilage: Making the cartilage surface smoother to reduce friction
- Autologous cartilage transplant: Taking a piece of cartilage from another part of the body and placing it in the knee
- Osteochondral autograft transplant: Using cartilage from a non-weight-bearing area to replace damaged cartilage in the knee
2. Torn Knee Ligaments
Knee ligament tears often result from a strong impact to the outside of the knee. Athletes involved in sports like hockey and football are at higher risk.
Treatment for Torn Ligaments:
- For partial tears:
- Using protective knee braces
- Strengthening exercises
- Avoiding activities that could cause more damage
- For severe tears or if initial treatments don’t help, surgery may be recommended.
3. Chondromalacia
Chondromalacia involves the deterioration of knee cartilage, reducing joint protection. This is common among runners and people who put constant stress on their knees.
Treatment for Chondromalacia:
- Over-the-counter pain relievers
- Applying ice to reduce swelling
- Using braces or tape for knee support
- Resting the knee
- If the knee doesn’t improve, a doctor might suggest arthroscopic surgery to smooth the cartilage.
4. Osteoarthritis
Osteoarthritis is the most common type of arthritis in the U.S., affecting 32.5 million adults. It involves the breakdown of protective cartilage in the joints, with no cure. In severe cases, joint replacement might be necessary.
Treatment for Osteoarthritis:
- Over-the-counter pain and anti-inflammatory medications
- Cortisone injections
- Physical or occupational therapy
- Lubricant injections
5. Patellar Tendinitis
Patellar tendinitis is an overuse injury affecting the tendon connecting the knee cap to the lower leg, causing a burning sensation and pain at the front of the knee.
Treatment for Patellar Tendinitis:
- Applying ice to reduce swelling
- Resting from running and jumping
- Strengthening exercises for the upper leg muscles
- Taking over-the-counter pain relievers
- Using a patellar tendon strap
- If these methods don’t work, doctors may recommend platelet-rich plasma injections or other interventions.
6. Iliotibial Band Syndrome (ITBS)
ITBS commonly affects runners and involves the iliotibial band rubbing against the outside of the knee.
Treatment for ITBS:
- Resting from running
- Massaging the iliotibial band, quads, and glutes
- Strengthening core, glutes, and hips
- Physical therapy
- Taking NSAIDs (non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs)
- Applying ice
- If other treatments fail, local steroid injections might be considered.
7. Patellofemoral Pain Syndrome (PFPS)
PFPS, also known as runner’s knee, causes pain in the front of the knee and is a common cause of knee pain.
Treatment for PFPS:
- Taking over-the-counter medications
- Using supportive braces
- Resting and avoiding stairs
- Exercises for hips, quads, and hamstrings
- Avoiding high-impact activities like running
- Focusing on low-impact exercises like swimming or stationary cycling
- In severe cases, doctors may recommend arthroscopic surgery.
8. Nerve Injury
Nerve inflammation or injury in the knee can also cause a burning sensation, often occurring from high-impact sports or knee surgery.
Treatment for Nerve Injury:
- Over-the-counter pain relievers
- Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs
- Applying ice to reduce swelling
- Steroid injections
- Surgery
Home Remedies for Burning Knee Pain
- Rest: Avoid stressing the knee to help it heal.
- Ice Therapy: Apply ice for 15-20 minutes to reduce swelling.
- Heat Therapy: Use a warm compress to relax muscles if there’s no swelling.
- Elevate: Keep your knee elevated to reduce swelling.
- Compression: Use an elastic bandage or knee brace for support.
- Gentle Exercises: Try low-impact activities like swimming or cycling.
- Stretching: Perform gentle stretches to maintain flexibility.
- Turmeric and Ginger: Consume for their anti-inflammatory benefits.
- Epsom Salt Soak: Soak in warm water with Epsom salts to relieve pain.
- Proper Footwear: Wear supportive shoes to reduce stress on your knees.
- Maintain Healthy Weight: Reducing excess weight can relieve knee pain.
- Massage: Gently massage the knee area to improve circulation.
When to See a Doctor for Burning Knee Pain
Most burning knee pain can be treated at home with rest, ice packs, and exercises to strengthen the muscles around the knee. However, if the burning sensation doesn’t improve after a few days or the pain gets worse, it’s important to see a doctor.
Your knees play a key role in moving, sitting, and bending. If you have severe pain or trouble moving your knee, these could be serious signs that need a medical check-up. A doctor might suggest further treatments like physical therapy or, in some cases, surgery to ensure long-term health and mobility.
Warning Signs to Watch For
Sometimes, burning pain in the knee can be a sign of a serious medical issue. If you experience any of the following symptoms, see a doctor right away:
- Weakness or numbness in your legs
- Problems with controlling urination or bowel movements
- Slurred speech
- Vision problems
- Fever
- Unexplained weight loss
- Severe pain, especially at night
If you can’t put weight on your knee or if there is significant swelling that prevents you from bending or straightening your knee, contact your doctor. If your pain or symptoms affect multiple parts of your body, it’s important to get checked by a professional.
Conclusion
Dealing with burning knee pain can be challenging and may negatively impact your daily life, making it hard to walk, rest, or sleep. Burning sensations, swelling, redness, and stiffness are common symptoms that might indicate issues such as arthritis or ligament injuries.
Understanding where the pain is located—whether in the front, side, or back of the knee—can help determine the cause and guide appropriate treatment. Common causes include cartilage damage, ligament injuries, chondromalacia, arthritis, patellar tendinitis, and iliotibial band syndrome.
In many cases, home treatments like rest, ice packs, and over-the-counter medications can help. However, if the pain persists or worsens, it’s important to see a doctor. Early diagnosis and treatment are crucial to avoid further problems and effectively manage your condition.
If you experience severe pain, weakness, numbness, or difficulties with urination or bowel control, these could be signs of a more serious issue, and you should see a doctor immediately. Timely treatment of knee pain can help maintain your mobility and quality of life.